Welcome to part two of my Windows 2003 terminal services article. This section will be of interest to terminal server administrators and clients. It includes a step-by-step guide of how to logon to a terminal server, troubleshooting common logon problems, and a tips section.
A Windows 2003 Terminal Server can be accessed by a windows client that has Remote Desktop Connection installed or via a web browser (remote desktop web connection).
Troubleshooting Logon Problems
Apart from the obvious logon error of typing in a wrong username or password, there exists two common problems that users come across when logging on. These are shown below.
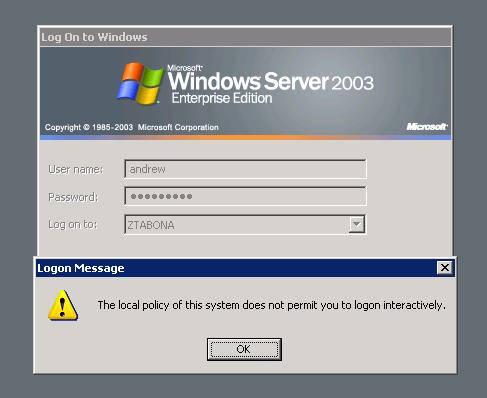
The local policy of this system does not permit you to logon interactively.
This error indicates that the group policy of the terminal server does not allow you to logon interactively. The settings will have to be changed from the group policy object editor by your administrator.
To do this, open gpedit.msc and navigate to the following section:
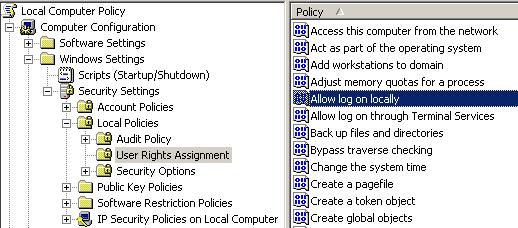
Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > User Rights Assignment
and after double clicking on the “Allow Log on Locally” from the Policy list, choose the user that you want to grant local log on access to and press OK. The image below indicates which section must be clicked on.
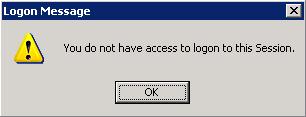
You do not have access to logon to this session.
The error message below means that you do not have access to logon to the terminal services session because your account has not been given the effective permissions from the terminal services manager on the server.
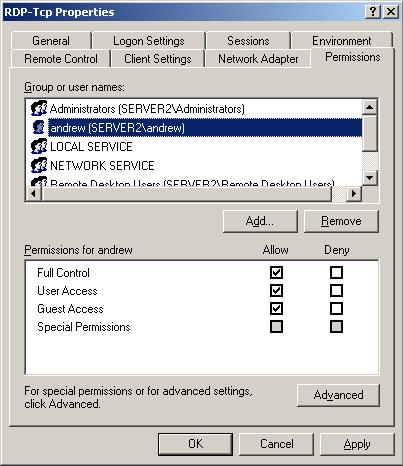
To correct this, open the Terminal Services Configuration, double click the RDP option in the main window and go to the permissions tab. Select Add and choose your account before pressing OK and assigning the right permissions to that account. Now attempt to logon again with that user account.
Terminal Services Client Logon – A step-by-step guide
Web Client
The terminal services web client will allow you to logon to a terminal server from your web browser. This is very handy as it provides quick and easy access from anywhere.
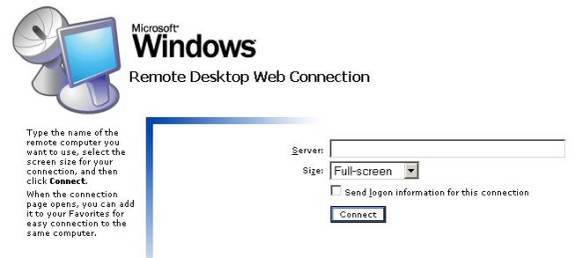
Open your web browser and in the address bar type the following details:
where server_name is the name of the terminal server (this can also be the IP address). If the WWW service and the tsweb website has been started on the server then you will be directed to a page like the one seen below:
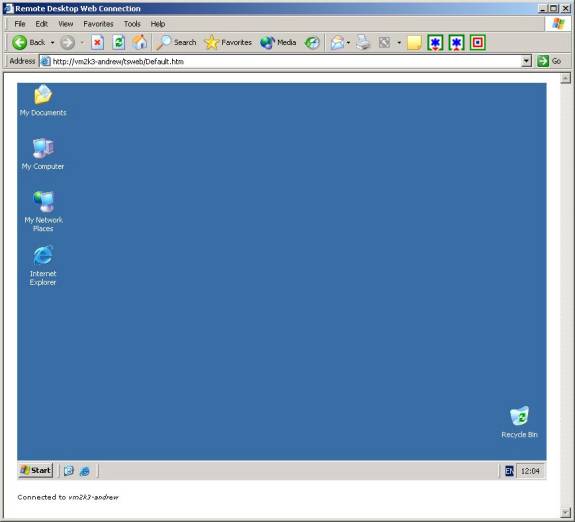
Enter the name of the server you want to connect to and choose the size of the screen before clicking ‘connect’. If you do not already have the required ActiveX component installed then you will be prompted to install it – click Yes when the window pops up and asks you to confirm the setup. In my example I have chosen for the screen to use a 800×600 display size. The web browser will act as a place holder for the terminal services screen to be displayed, as shown in the following screenshot.
Remote Desktop Connection
Remote Desktop Connection is installed by default on Windows XP- but can also be downloaded as a separate application from the Microsoft website. This is used to initiate a terminal services session from the client side. To open it type mstsc in the run box or navigate to Accessories > Communications on the Start menu.
The image below shows the general tab of the Remote Desktop Connection window, which was expanded by pressing the Options >>> button on the original window.
In this tab you can save your connection settings for future use, specify which computer you want to connect to and supply the logon credentials. The other tabs are used for performance related options like the display size and colour, speed and placement of resources.
Once you have entered the correct logon details press connect to initiate the session. It is likely that you will be asked to re-enter the logon credentials – unless the administrator has disabled the option from the terminal server.
10 Tips
- If you want to connect to a terminal server via the command prompt you can do so by typing the following: “mstsc -v:servername /F –console”. ‘mstsc’ represents the remote desktop connection executable file, -v specifies which server to connect to, /F is for full screen mode, and –console to indicate that you want to connect to the console.
- If you need to install a terminal services client for the MAC OS you can download it from here. Once it is setup, (given that you have network access and the right permissions) this will allow you to connect to a windows-based operating system running terminal services from a Macintosh computer.
- You can allow users to automatically logon to a session without having to type the username and password each time they initiate a connection. To do this two things have to be done.
- From the server side, open Group Policy Object Editor (gpedit.msc), double click Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Terminal Services and then choose Encryption and Security. Open the properties box of ‘Always prompt client for password upon connection’ and disable it.
- From the client side, open Remote Desktop Connection, and in the general tab enter the logon credentials in the appropriate boxes.
- The web client can be installed from the Add/Remove windows components. Go to the World Wide Web components section in the IIS 6.0 option. From there you can find and install Remote Desktop Web Administration.
- Available in the Windows 2003 resource kit is a self-extractable file called tsscalling.exe. This contains a set of tools that will aid with the scalability planning of terminal services.
- Each application you run uses up valuable resources, which might be needed by other users so close any programs or windows that you are not actively using.
- If you want to remotely restart a terminal server on the network you can use the tsshutdn command. The syntax is as follows:
tsshutdn wait_time /server: server_name /reboot /powerdown /delay: log_off_time
wait_time is the number of seconds you want to wait before the user is logged off from a session. The default time is 60.
server_name specifies the name of which terminal server you want to shutdown.
log_off_delay is the amount of time to wait, after users have been logged off from the session, before all processes are ended and the computer is shutdown. The default time is 30 seconds.
- Instead of just disconnecting from a session or closing the remote desktop window, log off – this will free up resources for other users.
- By default, Terminal Services runs on TCP and UDP port 3389. If for some reason you have to change that you can do so by open the registry editor (regedit.exe) and navigating to the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\WinStations\RDP-Tcp key. Look for the DWORD PortNumber and edit that to your needs.
- Run disk defragmenter on the terminal server to keep the disk clean, fast and ‘healthy’.
That concludes part two of the Windows 2003 terminal services article.
If utilized correctly, terminal services can be a quick, safe and reliable tool that will allow application sharing and remote administration to become part of the package that benefits an organization and allows administrators to be more flexible.
Got a project that needs expert IT support?
From Linux and Microsoft Server to VMware, networking, and more, our team at CR Tech is here to help.
Get personalized support today and ensure your systems are running at peak performance or make sure that your project turns out to be a successful one!
CONTACT US NOW